勃起功能障礙(erectile dysfunction, ED)是一個常見的問題,根據著名的麻州男性老年化研究(Massachusetts Male Aging Study)顯示40至70歲的男性大約50%的人有ED的問題。目前對於ED的治療,主要的選項是基於第五型磷酸二酯酶抑制劑(phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, PDE5i)的藥物治療。除此之外,其他的選項還包括真空吸引器、陰莖海綿體內注射藥物、尿道塞劑、人工陰莖植入、血管重建、低能量震波、濃縮血小板血漿治療以及幹細胞治療等。雖然口服PDE5i的效果不錯,但是仍然有30到40%的人無效,特別是那些糖尿病或是骨盆腔手術過的族群。此外PDE5i可能導致不良反應,而且某些病人也有禁忌症,例如吃硝酸鹽類藥物的病人。因此,對於發展更有效的ED治療選項的需求,目前仍然存有顯著的落差。
基因治療,是把外在的遺傳物質(genetic materials)導入體內細胞以代償或矯正異常基因功能的治療。基因治療應用於治療不同領域的疾病,最近愈受重視,相關研究的數量逐年增加,包括眼睛、肝臟、惡性腫瘤等各方面的領域都有。ED基因治療始於1997年,跟前述這些領域相比,研究數量只算中等,且最近幾年增加有限。原因可能是缺乏開發新的媒介傳遞方法與新的基因治療目標(target)。儘管如此,基因治療還是為人類帶來新的希望,2017年美國FDA第一次核准基因治療用來治療淋巴球白血病(lymphoblastic leukemia)、大B細胞淋巴癌(large B-cell lymphoma)、以及視網膜失養症(retinal dystrophy)。2019年核准用於治療攝護腺癌、脊髓肌肉萎縮症(spinal muscle atrophy)以及黑色素細胞癌。
基因治療用來治療ED有4大優勢:
- 陰莖是外露器官,分子目標基因可以直接打入海綿體組織內而不需經過體循環。
- 陰莖海綿體血管平滑肌細胞的周轉率相對較低,分子目標基因預期可以表現較久。
- 陰莖血管平滑肌細胞間是由gap junction聯結在一起,經由細胞間的物質傳遞,易達成整片平滑肌細胞協同作用,因此可以容許較低的細胞轉染率 (transfection rate)。
- 可以針對不同疾病對勃起過程的影響來選擇分子目標基因,把遺傳物質轉導到陰莖內以促進勃起反應。
基因傳遞系統:外在遺傳物質需要媒介(vectors)攜帶才能順利進入目標細胞,因此必須設計基因傳遞系統,一般可分為下列三種情形。
- 病毒媒介(viral vectors):治療ED最常用的載體,具有高轉染效率(transfection efficiency) 。常用的病毒包括adenovirus、Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV)、Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)、lentivirus、retrovirus等。免疫反應、致瘤性、價格昂貴為其主要缺點。
- 非病毒媒介(non-viral vectors):具有低免疫反應、高包裝容量(packaging capacity)、易製造、低成本的優點,但轉染效率低。
- 基因修改幹細胞(genetically modified stem-cells):分離、培養幹細胞到體外進行轉染後,再把幹細胞注射回目標組織中。具有低免疫反應、高轉染效率的優點,動物實驗已證明注射至陰莖海綿體的幹細胞可以成功分化為內皮細胞與平滑肌細胞。
分子目標(molecular targets)
正常的勃起生理功能,是以陰莖海綿體平滑肌鬆弛為核心,受到神經系統及血管系統的支應與調控。依照目前的臨床前研究顯示,各種受到激活後可以導致海綿體平滑肌放鬆或抑制海綿體組織纖維化的分子,都可以設計成為治療ED的目標(圖一)。
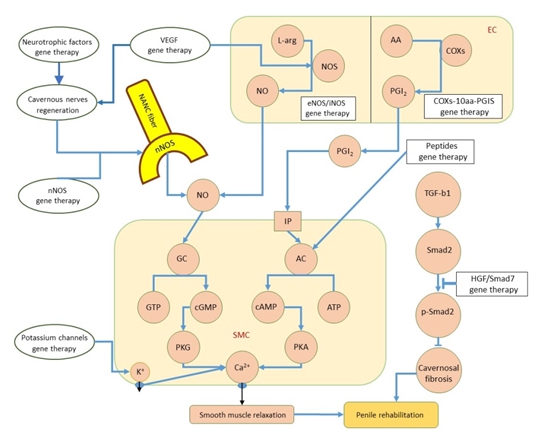
圖一、ED基因治療的分子目標全覽。神經營養因子(neurotrophic factors)與血管生成因子(angiogenic factors) 基因治療有助於海綿體神經的再生,進而增加陰莖nNOS的表現與神經元衍生的一氧化氮。另一方面,nNOS基因治療的效果與eNOS、 iNOS基因治療的效果類似,都是經由增進一氧化氮製造來媒介cGMP誘發的海綿體平滑肌鬆弛。此外,VEGF藉由活化PI3K/AKt/eNOS傳令路徑維持內皮細胞的活性與功能;COXs-10aa-PGIS基因治療可增進PGI2的製造來刺激cAMP誘發的平滑肌鬆弛以促進陰莖復健;胜肽基因治療則藉由活化腺苷酸環化酶(adenyl cyclase)來達成相同的功效。鉀離子通道基因治療直接調節海綿體平滑肌細胞內鈣離子濃度與穿越細胞膜的鈣離子通量,促成平滑肌鬆弛。HGF與Smad7基因治療則是經由抑制TFG-β1/Smad2路徑來改善海綿體纖維化,進而提升陰莖復健。
NANC fiber: non-adrenergic–non-cholinergic nerve fiber, EC: endothelial cell, SMC: smooth muscle cell, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor, L-arg: L-Arginine, NO: nitric oxide, NOS: nitrous oxide synthase, AA: arachidonic acid, PGI2: prostacyclin, COXs-10aa-PGIS: cyclooxygenase enzymes-10 amino acid residues-prostaglandin I2 synthase, PGI2: prostacyclin, IP: prostacyclin receptor, GC: guanylate cyclase, AC: adenylate cyclase, cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate, GTP: guanosine triphosphate, ATP: adenosine triphosphate, PKG: protein kinase G, PKA: protein kinase A, HGF: hepatocyte growth factor, TGF-β1: transforming growth factor beta 1, Smad: mothers against decapentaplegic homolog.
目前已知應用在ED基因治療的分子目標包括:一氧化氮合成酶(Nitrous Oxide Synthase, NOS)、神經營養因子(neurotrophic factors)、血管生成因子(angiogenic factors)、鉀離子通道、前列環素I2合成酶(prostacyclin I2 Synthase, PGIS)、抗纖維化因子(antifibrotic factors)、胜肽(peptides)等類別,治療效果大都為正向的。由於種類繁多,詳細的媒介、實驗方法、實驗模型與結果,簡單整理如下(表一至表四):
表一、一氧化氮合成酶路徑
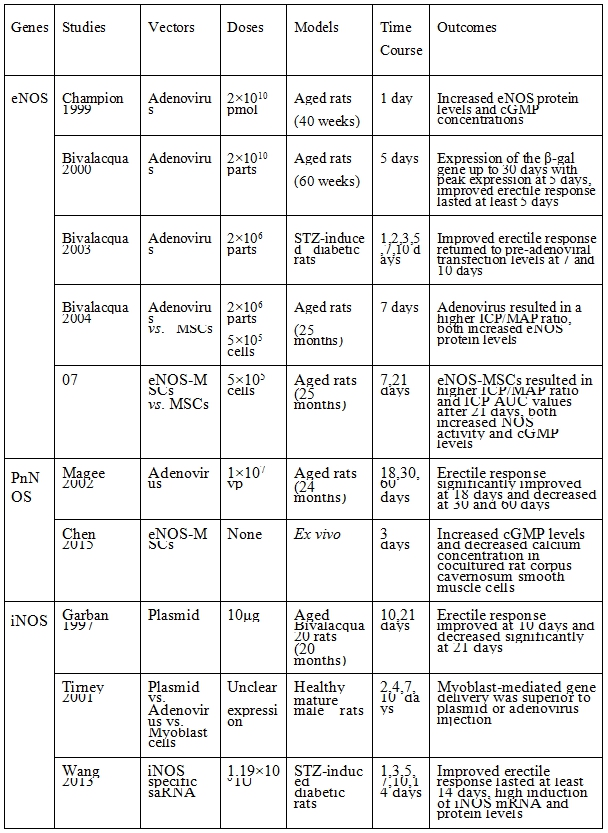
eNOS: endothelial nitrous oxide synthase, PnNOS: penile neuronal nitrous oxide synthase, iNOS: inducible nitrous oxide synthase, MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells, saRNA: small activating ribonucleic acid, cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate, β-gal: beta-galactosidase, ICP/MAP: intracavernous pressure/mean arterial pressure, ICP-AUC: area under the curve of intracavernous pressure, mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid.
表二、神經營養因子與血管生成因子路徑
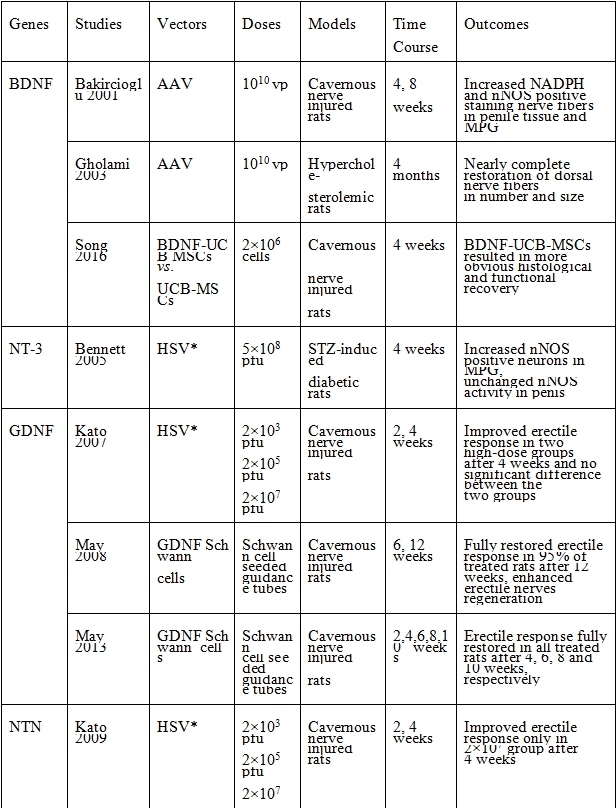
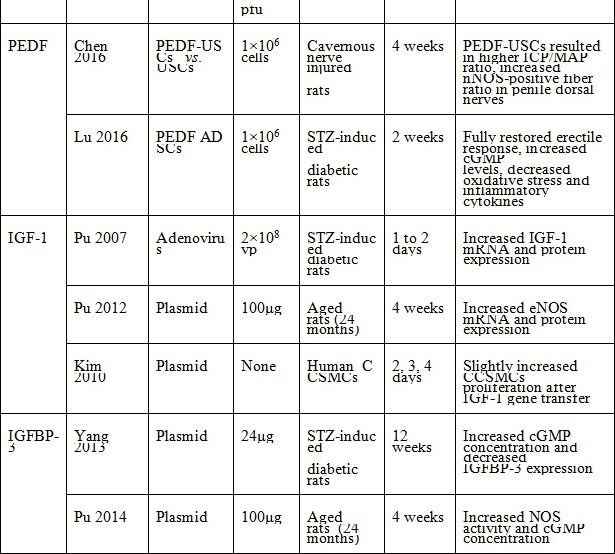
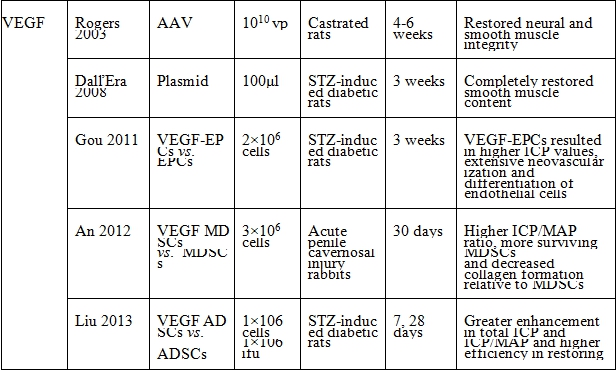
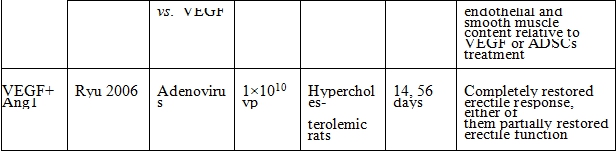
*Injection site was cavernous nerve injury sites.
BDNF: brain-derived nerve growth factor, NT-3: neurotrophin-3, GDNF: glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, NTN: neurturin, PEDF: pigment epithelium-derived factor, IGF 1: insulin-like growth factor-1, IGFBP-3: insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor, Ang1: angiopoietin-1, AAV: adeno-associated virus, HSV: herpes simplex virus, UCB-MSCs: umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells, ADSCs: adipose tissue-derived stem cells, USCs: urine-derived stem cells, endothelial progenitor cells, MDSCs: muscle-derived stem cells, CCSMCs: corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells, NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, nNOS: neuronal nitrous oxide synthase, eNOS: endothelial nitrous oxide synthase, MPG: major pelvic, EPCs: ICP: intracavernous pressure, ICP/MAP: intracavernous pressure/mean arterial pressure.
表三、鉀離子通道路徑
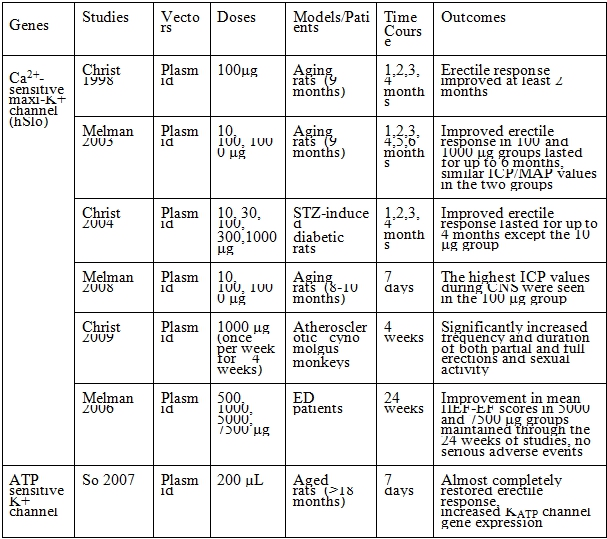
ED: erectile dysfunction, ICP: intracavernous pressure, ICP/MAP: intracavernous pressure/mean arterial pressure, CNS: cavernous nerve stimulation, IIEF-EF: international erectile function index-erectile function, KATP: ATP-sensitive K+ channel.
表四、其他分子目標路徑
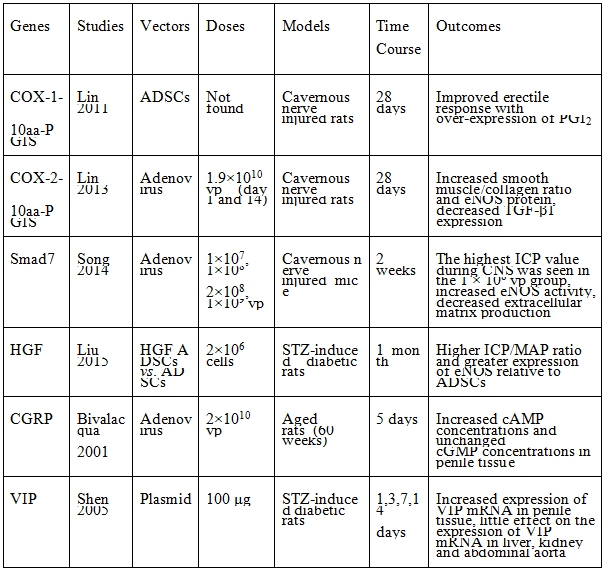
COX: cyclooxygenase enzyme, PGIS: prostaglandin I2 synthase, Smad7: mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7, HGF: hepatocyte growth factor, CGRP: calcitonin gene related peptide, VIP: vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, ADSCs: adipose tissue-derived stem cells, PGI2: prostacyclin, TGF-β1: transforming growth factor beta 1, eNOS: endothelial nitrous oxide synthase, ICP: intracavernous pressure, ICP/MAP: intracavernous pressure/mean arterial pressure, cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cAMP: cyclic adenosine mono phosphate, mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid.
結論:
雖然已經有很多研究結果帶來ED基因治療的希望,但都屬於臨床前試驗的階段,離臨床應用仍有一大段的距離。ED並非威脅生命的狀況,因此衛生主管機關對基因治療的安全性要求相當高,臨床試驗核准不易。目前唯一獲FDA核准進入臨床試驗第一期的研究,只有Melman於2006年發表,海綿體內注射hSlo DNA plasmid以增加人類Maxi-K channel在陰莖海綿體平滑肌的表現,結果顯示其安全性與初步效果。其他研究則尚未獲核准進行臨床試驗。基於ED病人的需求,特別是那些使用PDE5i無效者,基因治療仍需要更多的人員投入研究,革命尚未成功,同志仍須努力。
參考資料:
- Naoki Yoshimura, Ryuichi Kato, Michael B. Chencellor, Joel B. Nelson, and Joseph C. Glorioso. Gene therapy as future treatment of erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010; 10(9): 1305–1314.
- Botao Yu, Changjing Wu, Tao Li, Feng Qin, Jiuhong Yuan. Advances in gene therapy for erectile dysfunction: promises and challenges. Review Curr Gene Ther. 2018;18(6):351-365.
- Karl-Erik Andersson, George Joseph Christ. Gene therapy in erectile dysfunction: dead or alive? J Sex Med. 2020; 17(9):1587-1589.